Key Product metrics

- Published on
- /30 mins read/---
"What gets measured gets managed" ~ Peter Drucker
Introduction
Usually I hear people talking about metrics in the context of business, but what about product metrics? In this article, we will dive into the top 10 product metrics that will help you measure the success of your product. In a meeting context, when someone says 'I think' often indicates an opinion rather than a data-backed conclusion. Data is the oil of 21st century and analytics as an internal combustion engine.So Data is a product manager's best friend i,e most valuable tool for any decision makings.
| Category | # | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Business Metrics | 1 | Annual Recurring Revenue |
| 2 | Customer Lifetime Value | |
| 3 | Customer Acquisition Cost | |
| 4 | Churn Rate | |
| 5 | Retention Rate | |
| Product Metrics | 6.1 | Breadth,Depth, Frequency ,Usage |
| 6.2 | Breakage, Dormancy, Failure, Usage | |
| 7 | Feature Adoption & Retention | |
| 8 | Product Stickiness | |
| Customer Metrics | 9 | Net Promoter Score (NPS) |
| 10 | Mission Metric (ROI) | |
| 11 | North Star Metric |
1. ARR
Definition : Annual Recurring Revenue is used to measure the recurring revenue generated by a business annually, often in subscription-based or SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) business models. It provides insight into the stability and predictability of a company's revenue stream.
Why its useful
| Benefit | Why it matters | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Predictability and Stability | ARR provides a reliable, long-term view of recurring revenue, allowing businesses to forecast their financial future with confidence | A company with an ARR of 1 million can anticipate at least 1 million in revenue over the next year, assuming no churn or growth. |
| Measuring Growth | It helps track how well the business is growing over time by comparing it year-over-year. | If ARR grows from 1 million to 1.5 million in a year, it reflects a 50% growth rate, signaling healthy business performance. |
| Business Valuation | It is a key metric investors and stakeholders use to determine the valuation of subscription-based businesses. | A SaaS company with an ARR of 10 million and a 10x valuation multiple may be valued at 100 million. |
| Customer Retention and Expansion | Tracking ARR shows how much revenue comes from new customers, upselling, and retention versus how much is lost to churn. | A business with a high Net ARR Growth Rate (e.g., ARR growth after churn) demonstrates strong customer loyalty and effective upselling strategies. |
| Strategic Decision-Making | It helps businesses make critical decisions about pricing, product development, and market expansion. | If ARR growth is stagnant, a company might decide to invest more in sales and marketing or pivot to a new customer segment. |
| Aligning Cross-Functional Teams | ARR serves as a shared goal across teams (e.g., product, sales, marketing, and customer success) to drive revenue growth. | Product teams may focus on features that improve retention, while sales and marketing target strategies to acquire new customers and boost ARR. |
| Benchmarking and Performance Tracking | ARR provides a consistent metric for comparing performance against competitors or industry standards. | A SaaS company in the project management space can compare its ARR growth rate to similar competitors to assess its market position. |
| Identifying Red Flags | A decline in ARR indicates potential problems, such as high churn, ineffective sales strategies, or poor product-market fit. | If ARR decreases by 10% over a quarter, it may prompt an investigation into customer satisfaction or pricing issues. |
| Facilitating Fundraising | For startups and growing companies, ARR is a key metric used by investors to assess profitability and scalability. | A startup with strong ARR growth may secure funding more easily because it demonstrates sustainable revenue potential. |
Formula : ARR = Total Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) × 12
Example : Let's take Netflix as an example to calculate MRR.
Netflix Subscription Plans (Hypothetical Numbers)
Netflix offers the following subscription plans and subscribers:
Basic Plan: $10/month, 50 million Subscribers
Standard Plan: $15/month, 70 million Subscribers
Premium Plan: $20/month, 30 million Subscribers
Step 1: Calculate Revenue from Each Plan
Revenue from the Basic Plan : 50,000,000 × 10 = 500,000,000 $/month
Revenue from the Standard Plan: 70,000,000 × 15 = 1,050,000,000 $/month
Revenue from the Premium Plan: 30,000,000 × 20 = 600,000,000 $/month
Step 2: Total Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
MRR = Basic Plan Revenue + Standard Plan Revenue + Premium Plan Revenue
MRR = 500,000,000 + 1,050,000,000 + 600,000,000
MRR = 2,150,000,000 $
Step 3: Insights
Netflix generates
$2.15 billion in MRRfrom its subscription-based model.This metric helps Netflix forecast its
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR): ARR = MRR × 12 = $2.15 billion × 12 = $25.8 billion/year.
2. CLV
Definition : Customer Lifetime Value is the total revenue or profit generated by a customer over the entire course of their relationship with your business.It helps businesses understand the long-term value of their customers and make informed decisions about customer acquisition, retention, and product strategies.
Why its useful
| Benefit | Why it matters | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Drive customer retention efforts | CLV can help you pinpoint customers at the risk of churning and timely deploy targeted retention strategies, ultimately reducing customer attrition and encouraging repeat business. | As a lifecycle marketer, you find that customers with longer software subscription plans bring higher customer value to your business. So, to encourage long-term engagement with software buyers, you introduce a customer loyalty program that rewards buyers with exclusive benefits, such as premium support, personalized onboarding, and discounted renewal rates. |
| Improve customer acquisition | Discover the marketing channels and strategies that attracted your current high-value customers by calculating their customer lifetime value (CLV). It’ll give you insights on how to reach new leads as well as potential loyal prospects. | After calculating the CLV of customers acquired through various channels such as paid ads, social media, and referral programs, you find that customers acquired via referral programs have a higher CLV compared to others. So, you decide to invest more in referral programs to attract high-value customers. |
| Measure marketing effectiveness and return on investment (ROI) | By examining CLV growth, you can identify which campaigns generate the most favorable returns, ensuring that you allocate your budget to the most profitable initiatives. | As a content marketer, you notice that a specific content piece has resulted in a significant increase in conversions and a higher CLV. In response, you can make a case for your marketing department to allocate more resources to refine that content strategy to enhance overall marketing ROI. |
| Improves Customer Segmentation | CLV identifies which customer segments bring the most value, allowing businesses to target high-value customers. | As a SaaS marketer, you use CLV data to segment customers into different tiers based on their spending value and engagement level. You then create a campaign targeting segments with higher spending and higher engagement, offering specialized promotions and personalized content to them. |
| Drives Product and Service Improvements | Businesses use CLV to understand what features or services increase customer retention and satisfaction. | A gym finds that members who attend fitness classes have a CLV 30% higher than those who don’t.They introduce more classes and personalized training to boost CLV across their customer base. |
Formula : The formula can vary based on the business model. Here's the simplest version:
CLV = Average Purchase Value × Average Purchase Frequency × Customer LifespanExample : Subscription-Based Business (Netflix)
Netflix wants to acquire new customers and is considering spending more on marketing campaigns. To determine whether this investment is worthwhile, they calculate CLV.
Step 1: Calculate CLV
Assumptions:
- Average Monthly Subscription Fee: $15
- Average Customer Lifespan: 3 years (36 months)
- Gross Margin: 80% (after deducting costs like licensing and operations)
Using the CLV formula:
CLV = (Average Monthly Subscription × Gross Margin × Customer Lifespan)CLV = $15 × 80% × 36 = $432So, the average CLV per customer is $432.
Step 2: Compare CLV to CAC
Assumptions:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): $100 per new customer (cost of advertising, promotions, etc.)
Analysis:
CLV ($432) > CAC ($100)
This means Netflix earns $332 of profit per customer over their lifetime. Acquiring new customers at this cost is a profitable strategy.
Step 3: Business Decision
Now, Netflix has two options for a new marketing campaign:
- Campaign A: Costs $120 per new customer (higher CAC).
- Campaign B: Costs $80 per new customer (lower CAC).
Which campaign should Netflix choose?
- Campaign A’s CAC $120 is still less than CLV $432 , so it is profitable, but the profit margin is lower $432 - $120 = $312.
- Campaign B’s CAC $80 has a higher profit margin $432 - $80 = $352`.
Netflix would likely prioritize Campaign B unless Campaign A brings in higher value customers or expands into a new market.
3. CAC
Definition : Customer Acquisition cost is the total cost spent by business on acquiring a new customer.It's a crucial metric for understanding the efficiency and profitability of customer acquisition strategies, particularly in subscription-based or SaaS businesses.

Why its useful
| Benefit | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| Evaluate Profitability | CAC should be significantly lower than Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) to ensure profitability. |
| Optimize Marketing Spend | Helps identify which marketing channels or campaigns yield the best return on investment (ROI). |
| Strategic Decision-Making | Guides decisions on pricing, marketing budgets, and scaling efforts. |
| Investor Confidence | A low CAC compared to CLV signals a healthy and scalable business. |
Formula :
CAC = Total Cost of Sales and Marketing ÷ Number of New Customers AcquiredTotal Cost of Sales and Marketing: Includes marketing spend (ads, campaigns, content creation), sales team salaries, software/tools, and any other customer acquisition-related costs.
Example : Netflix wants to calculate its CAC for a month.
Assumptions:
- Marketing Spend: $500 million (e.g., digital ads, promotions, etc.)
- Sales Team Salaries: $10 million
- Software/Tools: $5 million
- New Customers Acquired: 2 million
Total Cost: $500M + $10M + $5M = $515M
CAC: $515M ÷ 2M = $257.50 per customer
Interpreting CAC:
- Compare CAC to CLV
- From the earlier Netflix CLV example, CLV = $540.
- CLV/CAC Ratio : 540÷257.50 ≈ 2.1
- A CLV/CAC ratio of 3:1 or higher is ideal, so Netflix may need to reduce CAC or increase retention.
- Channel-Specific CAC:
- If Netflix runs campaigns on multiple platforms, calculating CAC per channel reveals the most cost-effective ones.
IMPORTANT
As a general rule of thumb, a LTV:CAC ratio of 3:1 is a healthy industry benchmark.
Ways to Reduce CAC
- Optimize Marketing Spend: Focus on high-ROI channels (e.g., referral programs, organic traffic).
- Improve Conversion Rates: Streamline the onboarding and purchasing processes.
- Retarget Existing Customers: Upsell or cross-sell to reduce reliance on acquiring new customers.
- Leverage Partnerships: Collaborate with complementary brands to access new customers at a lower cost.
How CAC is connected to CLV
The CLV/CAC ratio is the primary metric that highlights how efficiently a business acquires customers and how profitable those customers are over time.
CLV/CAC Ratio = Customer Lifetime Value ÷ Customer Acquisition CostExample of CLV/CAC Connection
Scenario: A SaaS Product (e.g., Netflix)
- CLV: $540 (calculated previously)
- CAC: $257.50 (calculated previously)
- CLV/CAC Ratio: 540 ÷ 257.50 ≈ 2.1
Interpretation:
- Netflix earns $2.10 for every $1 spent on acquiring a customer.
- While the ratio is decent, Netflix should aim to:
- Increase CLV by improving retention (e.g., reducing churn or upselling).
- Decrease CAC by optimizing marketing spend.
4. Churn rate
Definition : Churn Rate measures the percentage of customers or subscribers who stop using a product or service over a given time period. It's a critical metric for subscription-based businesses (like SaaS or streaming services) because it directly impacts revenue, growth, and profitability.
Why its useful
| Benefit | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| Indicator of Product Health | High churn could signal poor product-market fit, pricing issues, or a lack of customer satisfaction. Low churn suggests strong customer loyalty and satisfaction. |
| Impacts Growth | High churn can offset new customer acquisition, making it harder to grow. if Netflix gains 10,000 new customers in a month but loses 8,000 the net growth is only 2,000. |
| Affects Lifetime Value (CLV) | Churn directly reduces customer lifespan, which in turn lowers CLV. |
| Cost Implications | Acquiring new customers (CAC) is more expensive than retaining existing ones. Reducing churn improves overall profitability |
Formula :
Churn Rate = (Customers Lost During a Period ÷ Total Customers at the Start of the Period) × 100Example : Netflix's Monthly Churn Rate
Assumptions:
- Netflix starts January with 100,000 subscribers.
- During January:
- 5,000 subscribers cancel their subscriptions.
- 10,000 new subscribers join.
- Total at the end of January = 105,000.
Churn Rate Calculation:
Churn Rate = (Customers Lost ÷ Customers at Start) × 100
= (5,000 ÷ 100,000) × 100
= 5%What Does It Imply?
Impact on Revenue:
- A churn rate of 5% means that the company loses 5% of its revenue (or subscription base) unless it acquires new customers or retains the existing ones.
- Example: If each customer pays $10/month, losing 5,000 customers means losing
5,000×10=$50,000.
Customer Retention:
- A churn rate of 5% means 95% of customers stay loyal during the same period.
- Higher churn rates (e.g., 10%) could indicate issues like dissatisfaction or strong competition.
Customer Lifespan:
- Churn rate is inversely related to customer lifespan.
- For a churn rate of 5%, the average customer stays for `1 ÷ 0.05 = 20 = 20 months.
Sustainability:
- If the company acquires fewer customers than it loses (e.g., gains 3,000 but loses 5,000), its user base shrinks.
A 5% churn rate may be considered good or bad depending on the industry:
SaaS or Subscription Businesses: Aim for churn rates below 3%-5% monthly.
Mobile Apps: Higher churn (e.g., 10%-20%) may be common due to casual usage.
Telecom: Monthly churn below 2% is desirable.
Strategies to Reduce Churn
- Improve Customer Onboarding
- Enhance Customer Support
- Offer Loyalty Programs
- Analyze Customer Behavior
- Implement Feedback Loops
5. Retention rate
Definition : Retention Rate measures the percentage of customers who continue to use a product or service over a specific time period. It’s the opposite of churn rate and indicates customer loyalty, satisfaction, and the overall health of a business.
Why Retention Rate matters
| Benefit | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| Customer Loyalty | A high retention rate means customers find value in the product and are likely to stay. Businesses with higher retention rates spend less on acquiring new customers. |
| Impacts Revenue | Retaining customers leads to more predictable revenue streams. Retained customers are more likely to engage in upsells or upgrades. |
| Cost Efficiency | Acquiring new customers (CAC) is 5–25 times more expensive than retaining existing ones. A focus on retention increases profit margins. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Retention directly impacts CLV. The longer customers stay, the higher the lifetime value. |
Formula :

Example :
Example: Retention Rate for Netflix
Scenario:
- Customers at Start of Month: 100,000
- New Customers Acquired: 20,000
- Customers at End of Month: 110,000
Apply the Formula
Retention Rate = (110,000-20,000)÷100,000 * 100
Retention Rate = (90,000)÷100,000 * 100
Retention Rate = 90%What does 90% Retention Rate means
- Netflix retained 90% of its existing customers during the month.
- 10% churned, meaning they canceled their subscriptions.
- If retention remains high, it ensures steady recurring revenue and a growing customer base.
Retention Strategies
To increase retention rate, companies can:
- Improve Onboarding: Ensure new customers experience value quickly.
- Engage with Personalization: Offer recommendations based on user behavior (e.g., Netflix suggests shows based on past viewing).
- Provide Exceptional Support: Quickly address issues to keep customers satisfied.
- Introduce Loyalty Rewards: Offer discounts or perks for long-term customers.
- Monitor Engagement: Identify and re-engage inactive customers with reminders or offers.
6. BDFU framework
BDFU is used in multiple contexts depending on the industry, framework, or company focus. There are 2 variations based on the context
6.1 Breadth, Depth, Frequency, Usage
Context: This version is used in engagement and feature adoption analysis, helping teams evaluate the extent and intensity of product usage.
Key Goal: Measure how users interact with the product in terms of the variety of features (breadth), how deeply they engage with specific features (depth), how often they use the product (frequency), and overall engagement (usage).
| Sl No | Definition | Measurement | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Breadth | Measures how many features or areas of the product users are engaging with | A user streams movies, watches TV shows, and explores documentaries. |
| 2 | Depth | Measures how deeply users engage with a single feature or function of the product | A user consistently watches one particular genre, like comedy, or completes entire series without dropping off |
| 3 | Frequency | Measures how often users engage with the product within a specific time period. It reflects stickiness. | A user logs in daily to stream content |
| 4 | Usage | Measures the overall usage or consumption of the product by a user. It’s a cumulative metric combining breadth, depth, and frequency. | A user spends an average of 10 hours per week streaming content across multiple genres and devices. |
Hence here BDFU is broader and focuses on overall engagement trends.
6.2 Breakage, Dormancy, Failure, Usage
Context: This version is commonly used in retention and user lifecycle analysis, particularly in SaaS or subscription businesses. It focuses on identifying points where users drop off or fail to engage.
Key Goal: Understand where users struggle or disengage (breakage, dormancy, failure) and drive them toward active engagement (usage).
| No | Definition | Measurement | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Breakage | Users who never complete the initial onboarding or activation process and fail to experience the core value of the product | A user signs up but never finishes creating their profile or selecting their first show. |
| 2 | Dormancy | Users who sign up and complete onboarding but become inactive or disengaged over time. | A user stops logging in because they feel the recommended content isn’t aligned with their interests. |
| 3 | Failure | Users who attempt to use the product but encounter obstacles or friction that prevents them from succeeding. | A user tries to stream a movie but faces buffering issues or errors on their device. |
| 4 | Usage | Users who actively use and engage with the product, achieving the intended value. | A user streams content daily, creates multiple profiles for family members, and rates movies they watch. |
Thus,this version focuses on user retention and lifecycle bottlenecks.
7. Feature Adoption & Retention rate
Definition : Feature adoption measures how well a specific feature in a product is being discovered, used, and integrated into users' regular workflows. It evaluates whether users are realizing the intended value of the feature.
Why its useful
Formula : Adoption Rate is the percentage of users who start using a specific feature out of the total user base.
Adoption Rate = (Number of Users Who Used the Feature ÷ Total Users) × 100Example : In a trading app like Zerodha, if 1,000 out of 10,000 users use a new charting tool, the adoption rate is
= 1,000÷10,000×100
= 10%Similarly Drop-Off Rate = (Users Who Abandon the Feature ÷ Total Users Who Tried the Feature) × 100
Retention Metric measures how well a product or feature keeps users engaged and coming back over time. It’s critical for long-term growth and customer loyalty.
Formula :
Retention rate = (UsersatEnofPeriod - NewUsers) ÷ UsersatStartofPeriod * 100Example : In Zerodha, if 10,000 users started using a feature in January and 8,000 continue in February (with 1,000 new users joining in February) ,then Retention rate is
Retention rate = (UsersatEnofPeriod - NewUsers) ÷ UsersatStartofPeriod * 100
= (8,000 - 1,000) ÷ 10,000 * 100
= 7000 ÷ 10,000 * 100
= 0.7 *100
= 70.0Hence the retention rate is 70% .
Relationship Between Feature Adoption and Retention
Adoption Drives Retention:
- If users adopt a feature and find value, they’re more likely to stay engaged and loyal to the product.
- Example: In a SaaS product, if users adopt an advanced reporting tool, it enhances their workflow, increasing their likelihood to retain.
Retention Provides Feedback on Adoption:
- High retention of users who adopt a feature indicates success.
- Low retention signals the feature might not be delivering sufficient value.
8. Product stickiness
Definition : Product stickiness refers to how well a product retains users by becoming an integral part of their daily routines or workflows. A "sticky" product is one that users rely on frequently, find value in, and are unlikely to abandon. High product stickiness typically leads to increased retention rates, engagement, and customer lifetime value (CLV).
Why its useful
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improves Retention | Sticky products keep users coming back, reducing churn. |
| Enhances Word-of-Mouth Growth | Users of sticky products are more likely to recommend them, driving organic growth. |
| Maximizes Revenue | Sticky products increase CLV by ensuring consistent engagement over time. |
| Defends Against Competitors | When a product becomes essential, users are less likely to switch to competitors (e.g., Excel for spreadsheets or Figma for design). |
Formula :
Stickiness Ratio = Daily Active Users (DAU) ÷ Monthly Active Users (MAU)Example :If Netflix has 10M DAU and 50M MAU ,then
Stickiness Ratio =DAU/MAU
= (10M ÷ 50M) × 100
= 20%Ideal Benchmark: 20%-30% is considered good for most products; higher ratios indicate greater stickiness.
A high retention rate is a sign of stickiness, as users continue returning to the product over time.
Case Study: Lets study an example of great stickiness product Zerodha, India’s leading stockbroking platform, is an excellent example of a sticky product in the financial and investment sector.
- Breadth of Offerings
- What It Means: Zerodha offers a wide range of features like equity trading, mutual funds, options, futures, and even goal-based investing through their platform Coin.
- Why It's Sticky:
- Users can fulfill multiple financial needs (trading, investing, goal planning) on a single platform.
- This reduces the need to switch to competitors or use multiple apps.
- Example: A trader uses Zerodha's Kite for intraday trading, while also using Coin for SIPs in mutual funds.
- Depth of Engagement
- What It Means: Zerodha deeply engages users with its intuitive and efficient trading tools like Kite and Console for advanced analytics.
- Why It's Sticky:
- Kite provides advanced charting tools and real-time data, making it indispensable for active traders.
- The Console dashboard gives a deep breakdown of portfolio performance, P&L reports, and tax reports.
- Example: A trader who starts using Kite for its superior charting tools is likely to stick because of its smooth UX and comprehensive features.
- Frequency of Usage
- What It Means: Zerodha caters to traders and investors, ensuring frequent engagement.
- Why It's Sticky:
- Daily Traders: Intraday traders use the platform multiple times a day for placing trades and analyzing market movements.
- Long-Term Investors: SIP reminders and market updates encourage periodic interactions.
- Example: A day trader logs into Kite every morning to analyze charts and place trades, while an investor checks their SIP performance monthly through Coin.
- Usage and Value Delivery
- What It Means: Zerodha consistently delivers value by offering low-cost services, educational resources, and seamless technology.
- Why It's Sticky:
- Low brokerage fees make it cost-effective for traders and investors.
- Educational initiatives like Varsity help users learn about stock markets and investing, increasing their trust and reliance on Zerodha.
- Example: A first-time investor learns the basics of stock markets through Varsity, opens a Zerodha account, and sticks with the platform due to its low fees and value-added tools.
Why Zerodha is a Sticky Product
Low Brokerage and Transparent Pricing
- Fixed brokerage of ₹20 per trade makes Zerodha an affordable choice for both small and large investors.
- Transparency in pricing builds user trust, reducing the likelihood of churn.
User-Centric Technology
- Kite's sleek, user-friendly design ensures ease of use, even for first-time investors.
- Tools like Streak (for algo trading) and Sensibull (for options trading) cater to advanced users.
Personalization
- Zerodha's platform provides personalized insights through Console, including P&L summaries, tax reports, and market notifications.
Community and Education
- Educational content through Varsity and engagement via community forums like TradingQnA helps users feel supported and part of a larger ecosystem.
Habit-Forming Features
- Regular notifications for SIPs, stock updates, and trade alerts encourage frequent usage.
- Investors and traders become reliant on the platform for their day-to-day financial activities.
9. NPS
Definition : Net Promoter Scoreis a widely used metric to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction by assessing how likely users are to recommend a product or service to others. It provides insights into customer sentiment and helps businesses identify promoters, detractors, and opportunities for improvement.
Why should Team track NPS
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Predicts Growth | Higher NPS indicates a loyal customer base likely to drive organic growth through referrals eg., Zerodha is the best example where users promoted the product to friends and colleagues |
| Identifies Pain Points | Low scores highlight areas where users are dissatisfied, allowing for targeted improvements. |
| Customer Segmentation | Categorizing users as promoters, passives, or detractors helps tailor engagement strategies. |
| Benchmarks Performance | Compare NPS with competitors or industry averages to understand relative performance. |
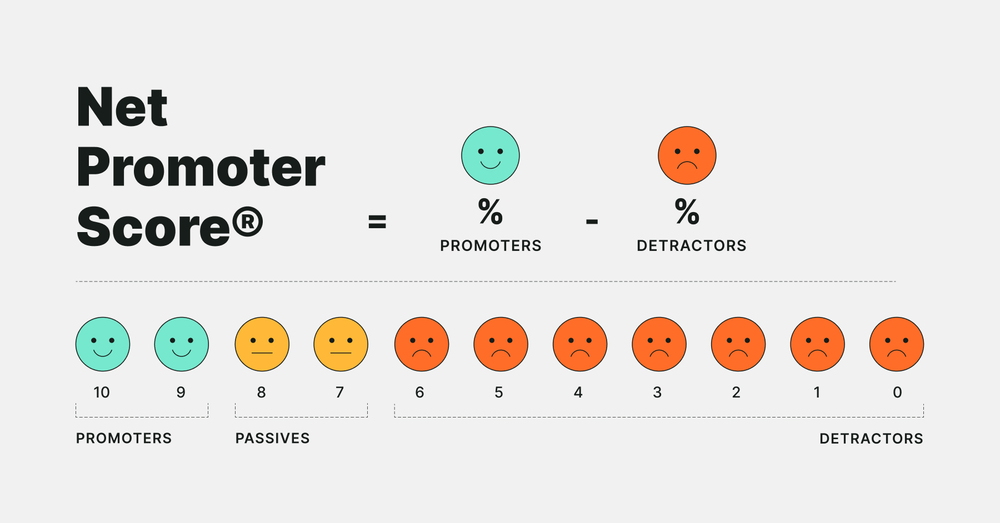
Formula :
NPS = % Promoters − % DetractorsScoring Categories:
- Promoters (9–10): Loyal customers who actively recommend the product and drive growth.
- Passives (7–8): Satisfied but unenthusiastic customers who may switch to competitors.
- Detractors (0–6): Unhappy customers who are unlikely to recommend the product and may discourage others.
NPS ranges from -10 to +10.
Example : NPS in Practice
Problem: Spotify wanted to understand how satisfied its users were and identify areas to improve.
Approach:
Sent an NPS survey to users asking: “How likely are you to recommend Spotify to a friend?”
Collected feedback, segmenting users into promoters, passives, and detractors.
Insights:
- Promoters loved personalized playlists like “Discover Weekly.”
- Detractors cited app crashes and missing features like lyrics.
Actions:
- Improved app stability and introduced real-time lyrics.
- Rewarded promoters with early access to new features.
Result: NPS score improved over time, correlating with increased user retention and growth.
10. Mission Metric
Definition : Customer Mission Metric is a metric that tracks how effectively a product helps customers achieve their core objectives or "mission" when using the product.
Unlike traditional business metrics (e.g., revenue or churn), this focuses specifically on measuring the success rate of the customer’s intended goal.It’s a customer-centric KPI that evaluates how well the product aligns with and delivers on customer needs and expectations.
Why its matters
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Customer-Centric Success | It emphasizes delivering value to users, not just meeting business goals. |
| Drives Retention and Loyalty | If customers consistently achieve their goals, they are more likely to stick with the product. |
| Differentiation | Understanding and achieving customer missions helps differentiate the product in a competitive market. |
| Aligns Teams | It keeps the product, design, and marketing teams focused on solving real user problems. |

Examples of Customer Mission Metrics
Zerodha (Trading App)
- Metric: Percentage of users who successfully execute trades without errors or drop-offs.
- Customer Mission: Enabling seamless and informed stock trading.
Uber (Ride-Hailing App)
- Metric: Percentage of rides completed without delays or cancellations.
- Customer Mission: Ensuring users get to their destinations quickly and reliably.
Amazon (E-Commerce)
- Metric: Percentage of orders delivered on time and in good condition.
- Customer Mission: Helping users receive desired products quickly and conveniently.
How to Measure Customer Mission Metrics
Understand the Customer Journey:
- Map the steps users take to achieve their goals.
- Identify points where success or failure occurs.
Define Success Criteria:
- Success should be measurable.
- Example: For a project management tool, success could be completing a task or achieving a project milestone.
Collect Data:
- Use analytics, surveys, and feedback to track outcomes.
- Example: Ask users if they successfully achieved their goals after using the product.
Analyze Success and Failure Rates:
- Identify the percentage of users achieving their goals.
- Analyze failure points to make improvements.
11. North Star Metric
Definition :The North Star Metric is a single, overarching metric that represents the core value your product delivers to users and aligns your team around a shared goal.
It focuses on the desired customer outcome rather than business outcomes like revenue or profit, driving long-term growth and user satisfaction.
Why its matters
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Customer-Centric | Reflects the value your product delivers to users. |
| Growth-Driving | Correlates with sustainable business growth. |
| Easy to Measure | The metric should be clear and trackable using available data. |
| Focuses on Long-Term Impact | Helps teams avoid short-term optimizations that might harm long-term user satisfaction. |
Examples of North Star Metrics by Industry
- Streaming Platforms (e.g., Netflix, Spotify)
- NSM: Hours of content consumed per user per week.
- Why: Reflects user engagement and satisfaction with the content library.
- E-Commerce Platforms (e.g., Amazon)
- NSM: Number of purchases per active customer per month.
- Why: Indicates customer satisfaction, repeat usage, and convenience.
- SaaS Tools (e.g., Slack, Notion)
- NSM: Number of messages sent per user per day (Slack).
- Why: Shows how integral the tool is to users' workflows.
- Fintech Apps (e.g., Zerodha, Robinhood)
- NSM: Number of trades executed per user per month.
- Why: Tracks how often users achieve their trading goals through the platform.
- Fitness Apps (e.g., Strava, Fitbit)
- NSM: Number of active days logged per user per month.
- Why: Encourages users to stay consistent with fitness goals.
Real time example of how Zerodha, or a similar trading platform, can define and use a North Star Metric (NSM) to align its teams, measure success, and drive growth:
Step 1: Identify the Core Value Proposition
What does Zerodha deliver to its users?
- Zerodha helps users make informed trades and invest seamlessly in stocks, mutual funds, and other financial instruments.
- The core value is enabling users to successfully participate in financial markets and grow their wealth.
Step 2: Define Zerodha's North Star Metric
Potential NSM:
- "Number of Successful Trades Executed Per User Per Month"
- Why?
- It reflects user engagement (active trading).
- It aligns with the business goal of increasing trading volumes, which directly impacts Zerodha's brokerage revenue.
- Successful trades indicate that users find the platform reliable, efficient, and valuable.
Step 3: Break Down the NSM into Contributing Metrics
The NSM can be supported by secondary metrics that track different parts of the user journey
- User Onboarding Metrics:
- Metric: Percentage of new users completing account setup (e.g., KYC completion).
- Why It Matters: Ensures more users are onboarded and ready to trade.
- Feature Adoption Metrics:
- Metric: Percentage of users using advanced tools like charting, Basket Orders, or Streak (algo trading).
- Why It Matters: Users adopting these tools are more likely to execute trades.
3. Retention Metrics:
- Metric: Monthly Active Traders (MAT).
- Why It Matters: Higher retention shows that users consistently engage with the platform.
4. Transaction Success Rate:
- Metric: Percentage of trades executed without errors.
- Why It Matters: A seamless trading experience builds trust and loyalty.
- Revenue Metrics:
- Metric: Average brokerage earned per user per month.
- Why It Matters: Higher trading activity aligns with Zerodha's revenue growth.
Step 4: How to Use the North Star Metric
Align Teams Around the NSM:
- Product Team:
- Focus on improving tools (e.g., charting, data analytics) that help users trade confidently.
- Marketing Team:
- Target campaigns to attract active traders who align with the NSM.
- Engineering Team:
- Optimize system performance to ensure trade execution is fast and error-free.
- Product Team:
Analyze User Behavior:
- Identify user segments:
- High-value traders: Focus on advanced tools.
- Infrequent users: Encourage engagement through education or reminders.
- Use behavioral data to see why some users aren't trading.
- Identify user segments:
Improve Key Features to Drive the NSM:
- Simplify onboarding to reduce friction for new users.
- Provide better educational resources (e.g., Varsity or webinars) to help users make informed trades.
- Add personalization, like recommending stocks or funds based on user preferences.
Track and Iterate:
- Regularly monitor the NSM and contributing metrics.
- Use A/B testing to validate changes that impact the NSM (e.g., introducing new trading features or simplifying workflows).