Recap
In the last blog feature prioritization -1 , we explored the importance of feature prioritization, why it is essential, and highlighted a few key examples; in this post, we will delve deeper into additional and other frameworks for other feature prioritization.
Eisenhower Matrix
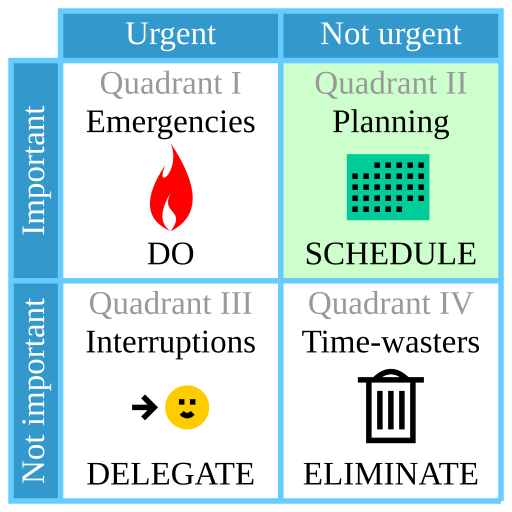
Based on U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower :This framework is particularly useful for time management and prioritizing tasks based on their urgency and importance ,sorting out less urgent and important tasks which you should either delegate or not spend much time on.

The Four Quadrants of the Eisenhower Matrix
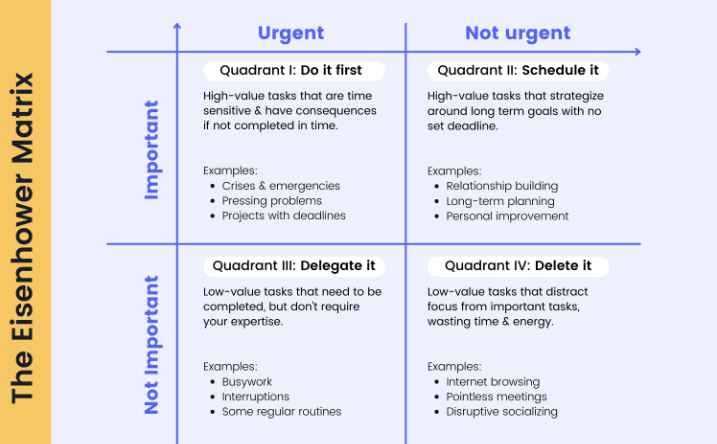
Quadrant 1: Urgent and Important (Do First):
Definition: Tasks that are both urgent and important. These require immediate attention and are crucial to achieving your goals.
Examples: Crises, deadlines, pressing problems.
Action: Do these tasks as soon as possible.
Quadrant 2: Not Urgent but Important (Schedule):
Definition: Important tasks that are not urgent. These contribute to long-term goals and development.
Examples: Planning, strategy, learning new skills, relationship-building.
Action: Schedule these tasks for a later time, as they are critical for long-term success.
Quadrant 3: Urgent but Not Important (Delegate):
Definition: Tasks that are urgent but not important. They often distract from your main goals.
Examples: Interruptions, some emails or calls, requests from others.
Action: Delegate these tasks to others if possible, or minimize the time spent on them.
Quadrant 4: Not Urgent and Not Important (Eliminate):
Definition: Tasks that are neither urgent nor important. These are often time-wasters.
Examples: Busywork, trivial activities, excessive internet browsing.
Action: Eliminate or reduce these tasks, as they do not contribute to your success.
Benefits of the Eisenhower Matrix
- Clarifies Priorities: Helps you see which tasks are truly important versus those that feel urgent but aren’t crucial.
- Improves Time Management: Encourages focusing on tasks that matter most and reduces time spent on non-essential activities.
- Reduces Stress: By clearly organizing tasks, you can avoid the overwhelm that comes from handling too many things at once.
Example:Imagine you’re a Product Manager
Pros:
Clarity and Focus: The Eisenhower Matrix provides a clear structure for decision-making by categorizing tasks into four quadrants.This helps in identifying what truly needs immediate attention and what can be deferred or delegated.
Improves Productivity: By focusing on important tasks, especially those that are not urgent (Quadrant II), users can work on strategic goals and prevent crises from occurring, ultimately leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Reduces Stress: Prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance can reduce the overwhelming feeling that comes with having too many tasks. By tackling high-priority tasks first, you can alleviate stress and maintain better control over your workload.
Encourages Delegation: The Matrix promotes effective delegation by helping users identify tasks that are urgent but not important (Quadrant III). Delegating these tasks allows individuals to focus on more critical activities.
Enhances Long-term Planning: By regularly using the Eisenhower Matrix, users are encouraged to focus on long-term goals and strategic planning, rather than just reacting to immediate issues.
Cons:
- Oversimplification: The Matrix categorizes tasks into only four quadrants, which might oversimplify complex tasks or situations. Some tasks might not fit neatly into one category, making the decision process more challenging.
- Subjectivity: The determination of what is "important" or "urgent" can be subjective and may vary from person to person. This subjectivity can lead to inconsistent prioritization, especially in team settings.
- Neglect of Quadrant II: While the matrix emphasizes the importance of Quadrant II (Important/Not Urgent), users may still gravitate towards urgent tasks, neglecting important but non-urgent tasks that are crucial for long-term success.
- Does Not Consider Task Dependencies: The matrix does not account for tasks that are dependent on others or require sequential completion, which can be a limitation in more complex project management scenarios.
- Time-Consuming: Regularly categorizing tasks into the matrix can become time-consuming, particularly if you have a large number of tasks or if your priorities frequently change.
Cost Of Delay
Cost of Delay (CoD) It measures the financial (economic impact)or opportunity loss caused by delaying the delivery of delaying a project or feature. It helps prioritize work by focusing not just on the value of delivering something, but also on the cost of not delivering it in a timely manner.
Key Concepts
- Value: This is the benefit or revenue that a feature or project is expected to generate.
- Time Sensitivity: This represents how quickly the value of a feature decreases over time. Some features are more time-sensitive than others.
- Urgency: This is the degree to which a delay impacts the overall value. Higher urgency means a higher cost of delay.
Why Cost of Delay Matters
Informed Prioritization: It helps teams prioritize features or projects that are time-sensitive and would result in higher economic losses if delayed.
Resource Allocation: It guides resource allocation towards work that will have the greatest economic impact if delivered sooner.
Focus on Value: It shifts focus from simply delivering features to delivering them at the right time to maximize value.
The formula for calculating Cost of Delay is:
//CoD is the overall economic impact of delay on the success of a project or product on the market
Cost of Delay = Economic Value * Time sensitivity * Duration of DelayHowever, in many practical applications, teams use simpler approaches:
- Simple Numerical CoD:
- Assign a dollar value to the potential revenue or cost savings a feature would generate.
- Estimate how much value is lost per time unit (e.g., per week or month) if the feature is delayed.
- Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF): WSJF is a prioritization method used in Agile to help teams determine the order in which to work on features or tasks.
WSJF = Cost of Delay / Job Duration- Prioritize the work with the highest WSJF score, meaning it provides the most value in the shortest time or with less effort.
Types of Cost of Delay
- Immediate Cost of Delay: Losses that begin as soon as a feature is delayed, such as lost sales or penalties.
- Future Cost of Delay: Potential future revenue or benefits that are reduced or lost because a feature is delivered late.
- Accumulated Cost of Delay: Continuous and cumulative losses over time until the feature is delivered.
Visualizing Cost of Delay
- CoD Curve: This curve illustrates how the value of a feature diminishes over time. A steep curve indicates high urgency, meaning delays significantly decrease the potential value.
- Cost of Delay Profiles:
- Standard Profile: Value decreases at a constant rate over time.
- Accelerating Profile: Value decreases slowly at first but then accelerates rapidly.
- Fixed Deadline Profile: Value remains stable until a certain deadline, after which it drops sharply.
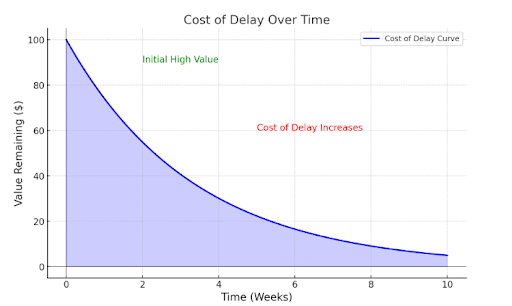
- The blue curve represents how the value of a feature decreases as time progresses.
- Initially, the feature holds high value, but as time passes (e.g., due to delays), the value diminishes, highlighting the increasing cost of delay.
This visual helps to understand that the longer a valuable feature is delayed, the more potential value is lost, emphasizing the importance of timely delivery.
Scenario : E-commerce Platform's Holiday Season Sale
An e-commerce platform is planning a feature to enable personalized product recommendations during its holiday season sale. The feature is estimated to increase sales by 10% due to better user engagement.
Cost of Delay Calculation:
Feature implementation time: 4 weeks
Revenue generated per day during the holiday season: ₹10,00,000
Expected revenue increase due to the feature: 10% or ₹1,00,000/day
Duration of the holiday season: 30 days
Economic Value = Total expected monetary value the feature generates= 30 days * 1,00,000 = ₹30,00,000
Time Sensitivity = A number between 0 and 1 indicating how critical the feature's timing is. 1 means high urgency (e.g., features for a holiday sale). 0.5 or lower for less time-critical features= 1
Fraction of Delay = =
COD = Economic Value * Time sensitivity * Duration of Delay
COD = ₹1,00,000 * 1 * 7 days = ₹7,00,000 If the team delays the feature launch by just 1 week, the platform loses ₹7,00,000 in potential revenue.
Prioritization Decision
- Continue working on lower-value maintenance tasks (e.g., bug fixes with no direct revenue impact).
- Cost of Delay: ₹7,00,000 for every week of delay.
- Focus the team on delivering the personalized recommendation feature by reallocating resources.
- This avoids the significant CoD and maximizes revenue during the critical sale period.
Scenario: Prioritizing Features for an E-Commerce App
You are a Product Owner for an e-commerce platform, and your development team has a few upcoming tasks. These tasks need to be prioritized for the next sprint, but the challenge is that there’s limited development capacity. You want to maximize business value while considering the effort required for each task.
Upcoming Tasks:
Task 1: Search Functionality Improvement
- Cost of Delay (CoD): ₹50,00,000 (High impact on revenue because a better search experience can drive more sales and improve user engagement.)
- Effort: 7 days of development effort.
Task 2: Bug Fix for Checkout Process
- Cost of Delay (CoD): ₹1,00,00,000 (Very critical bug that directly impacts revenue, as users can't complete purchases.)
- Effort: 2 days of development effort.
Task 3: Wishlist Feature
- Cost of Delay (CoD): ₹30,00,000 (Medium impact. Users often add items to wishlists, but it’s not as crucial as the checkout process.)
- Effort: 5 days of development effort.
Task 4: Payment Gateway Integration (New Option)
- Cost of Delay (CoD): ₹40,00,000 (Important, but not as urgent as fixing checkout issues.)
- Effort: 6 days of development effort.
Step 1: Calculate WSJF for Each Task
- use the formula WSJF =
- Task 1: Search Functionality Improvement
- WSJF = = ₹7,14,285.71
- Task 2: Bug Fix for Checkout Process
- WSJF = = ₹50,00,000
- Task 3: Wishlist Feature
- WSJF = = ₹6,00,000
- Task 4: Payment Gateway Integration
- WSJF = = ₹6,66,666.67
Step 2: Prioritize
- The Task with the highest WSJF score should be prioritized first.
- Task 2 (Bug Fix for Checkout Process) has the highest WSJF of ₹50,00,000. This task is crucial because it directly affects revenue by preventing purchases, so it must be prioritized first.
- Task 1 (Search Functionality Improvement) comes next, with a WSJF of ₹7,14,285.71. It has a high impact on sales, so it should follow.
- Task 4 (Payment Gateway Integration) should come next, with a WSJF of ₹6,66,666.67.
- Task 3 (Wishlist Feature) has the lowest WSJF of ₹6,00,000, so it will be the last feature worked on.
Step 3: Final Priority Order (based on WSJF):
- Task 2 – Bug Fix for Checkout Process (₹50,00,000 CoD, 2 days effort)
- Task 1 – Search Functionality Improvement (₹50,00,000 CoD, 7 days effort)
- Task 4 – Payment Gateway Integration (₹40,00,000 CoD, 6 days effort)
- Task 3 – Wishlist Feature (₹30,00,000 CoD, 5 days effort)
Task 2 (Bug Fix for Checkout) has the highest WSJF hence delaying it impacts revenue the most, and it’s a critical issue that must be fixed immediately to prevent customers from abandoning the checkout process. Task 1 also has a significant impact, but since it's not as urgent as Task 2. Task 4 not time sensitive as other task and Task3 is low priority.
In real-world product development, teams often have limited resources (time, developers, etc.), and prioritizing tasks based on business impact and effort is crucial. WSJF helps the team focus on delivering the most value with the least effort, optimizing the overall return on investment.
To effectively use CoD:
Estimate the economic impact: Determine the value of delivering the feature or project on time.
Understand time sensitivity: Evaluate how quickly the value decreases with delay.
Apply WSJF if necessary: Use the WSJF method to combine CoD with job duration for more nuanced prioritization.
Cost of Delay is a powerful tool that helps organizations focus on delivering value at the right time by considering the economic impact of delays. It aligns the team's priorities with business objectives, ensuring that the most time-sensitive and valuable work is prioritized.
Conclusion
Feature prioritization determines where you invest your time and resources, directly impacting your product's success.While these factors provide a solid foundation, common sense and careful evaluation are essential. Consider the bigger picture, analyze potential risks, and make informed decisions that maximize impact and minimize waste.
By effectively prioritizing features, your team can build a better product, achieve business goals, and deliver exceptional value to your users.
If you've made it this far , thanks for reading! Feel free to reach out if you'd like to chat more
